|
SD ID: Pan-Cancer Analyses & Cloud Computing within the EOSC ORGANISATION: Genome Biology Unit, European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) CONTACT: Sergei Iakhnin Email: llevar(at)gmail.com |
OVERVIEW:
There are a multitude of challenges being faced in the life sciences, health, food, fishery and agriculture sectors. In cancer research, Europe has taken a technical lead within international consortia around cloud-based pan-cancer genomic analysis. This global competitive advantage can be maintained by leveraging open science analysis models around controlled access data sets developed in collaboration with researchers elsewhere in the world. These analysis frameworks could also be re-used to analyse cardiovascular and neuro-degenerative diseases as well as stimulating biotech/pharmaceutical industries to use public cancer genomic data in R&D.
CONTEXT:
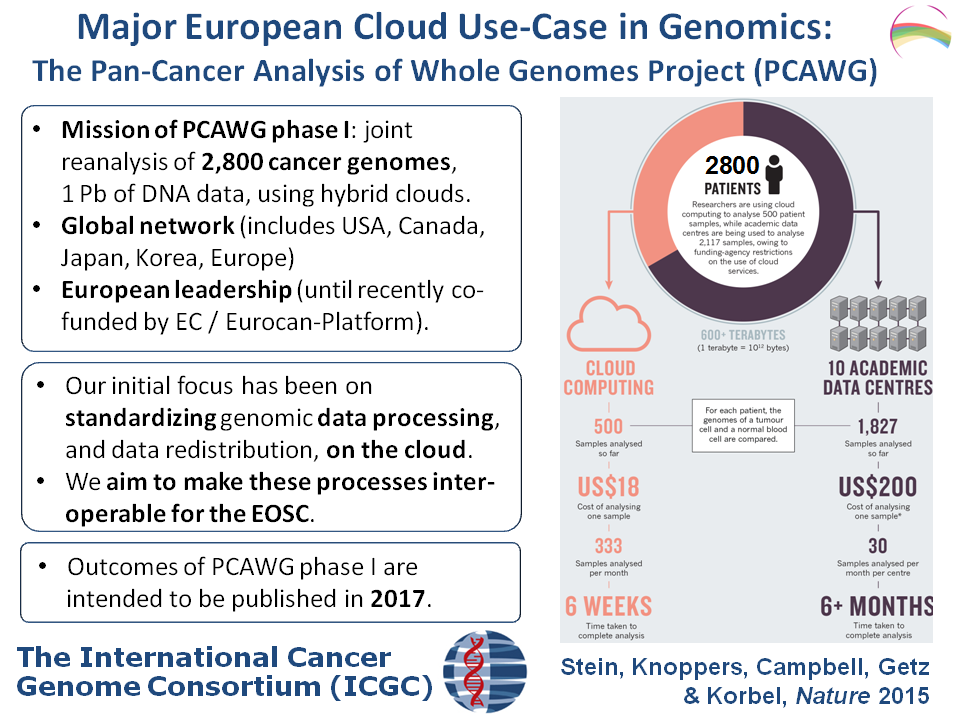
The pan-cancer analysis of whole genomes project (PCAWG) is analysing large cohorts of cancer genomes, and pursuing so-called pan-cancer studies to identify factors that may be involved in tumour formation and disease progression across multiple cancer types. PCAWG is currently analyzing >2800 cancer whole genomes, largely on academic and public clouds, and is also developing approaches for data integration with transcriptome & clinical data to address specific hypotheses.
The EOSCpilot science demonstrator aims to establish a portable cloud-based federated solution for collaborative cancer genomics and associated health data management, and an environment accessible to European scientists for analysis.
OBJECTIVES:
PanCancer aim is to develop interoperable IT frameworks to enable standardized sharing and large-scale processing of cancer genomes with other molecular and clinical data, to enable biological and translational breakthroughs. To do so, interoperable frameworks have been employed to process ~10,000 cancer Whole Genome Sequenced (WGS) tumour-normal pairs from 20most common cancer types. The main research objective is to uncover genome-wide patterns of different types of genetic variation, which requires availability of WGS data, and integrating these with molecular, demographic and clinical data. PanCancer will allow to proactively create suitable standards and interoperability.

MAIN ACHIEVEMENTS:
The Butler scientific workflow framework has been set up and tested at three globally distributed cloud computing environments that are based on the OpenStack platform, these include: the EMBL-EBI Embassy Cloud in the UK, the Cyfronet cloud in Poland, and the ComputeCanada cloud in Canada.
- >400 high coverage whole genome samples (~60 TB of data) from the ICGC pediatric brain cancer cohort were downloaded to the ComputeCanada cloud and
- ~50 TB of public data from the 1000 Genomes project was loaded onto the Cyfronet environment from the EMBL/EBI data servers utilising Cyfronet’s Oneprovider software.
- Butler was used to run a genomic alignment workflow (based on BWA and developed at The Sanger Institute) on >400 samples at ComputeCanada and >400 samples at EMBL/EBI Embassy cloud, with over 100 TB of data processed to date. Proper operation of the infrastructure was monitored by Butler’s detailed monitoring and self-healing capabilities.
IMPACT:
Engagement in the EOSC will enable Europe to maintain its current global competitive advantage in pan-cancer analyses & foster cloud-based solutions for genomic data analysis. Broader impact and the ability to reuse solutions in other areas (e.g. for cardiovascular & neuro-degenerative diseases) is also foreseen.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION
- Improve the availability of computational resources
- Improve systems’ stability and storage capabilities
- Introduce clear Service Level Agreements between service providers and service consumers to make clear the requirements asked by the consumers can be met